Hammer Toe Hereditary Causes
 Overview
Overview
Hammertoes usually start out as mild deformities and get progressively worse over time. In the earlier stages, hammertoes are flexible and the symptoms can often be managed with changes in shoe styles and foot care products. But if left untreated, hammertoes can become more rigid and painful. Corns are more likely to develop as time goes on-and corns never really go away, even after trimming. In more severe cases of hammertoes, corn lesions may evolve into severe ulcerations. These lesions frequently occur in patients who have vascular disease or are Diabetic with neuropathy. The ulcerations can extend to the bone and result in infection and possible loss of digit or amputation.
Causes
A hammertoe is formed due an abnormal balance of the muscles in the toes. This abnormal balance causes increased pressures on the tendons and joints of the toe, leading to its contracture. Heredity and trauma can also lead to the formation of a hammertoe. Arthritis is another factor, because the balance around the toe in people with arthritis is so disrupted that a hammertoe may develop. Wearing shoes that are too tight and cause the toes to squeeze can also be a cause for a hammertoe to form.
 Symptoms
Symptoms
The most obvious symptoms of this injury will be the the middle toe joint is permanently bent at an angle. In the beginning movement may still be possible but as time passes and the injury worsens the toe will be locked in place and possible require hammer toe correction surgery to fix. Another key indicator of hammer toe is that a lump or corn will form on top of the toe. The toe joint will be painful and walking can cause severe discomfort. Occasionally a callus may form on the sole of the injured foot. If you see any of these symptoms together or have been enduring pain for some time, seeing a podiatrist should be your next step.
Diagnosis
Most health care professionals can diagnose hammertoe simply by examining your toes and feet. X-rays of the feet are not needed to diagnose hammertoe, but they may be useful to look for signs of some types of arthritis (such as rheumatoid arthritis) or other disorders that can cause hammertoe. If the deformed toe is very painful, your doctor may recommend that you have a fluid sample withdrawn from the joint with a needle so the fluid can be checked for signs of infection or gout (arthritis from crystal deposits).
Non Surgical Treatment
If your hammertoe problem is diagnosed as flexible hammertoe, there are a number of nonsurgical treatments that may be able to straighten out your toe or toes and return them to their proper alignment. Padding and Taping. Your physician may pad the boney top-part of your hammertoe as a means of relieving pain, and may tape your toes as a way to change their position, correct the muscle imbalance and relieve the pressure that led to hammertoes the hammertoe's development. Medication. Anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin and ibuprofen can help deal with inflammation, swelling and pain caused by your hammertoe. Cortisone injections may be prescribed for the same purpose. If your hammertoe is a consequence of arthritis, your physician may prescribe medications for that.
Surgical Treatment
Surgical correction is needed to bring the toe into a corrected position and increase its function. Correction of the hammer toes is a simple outpatient surgery, with limited downtime. The best option is to fuse the deformed and contracted toe into a straight position. This limits the need for future surgery and deformity return. A new pin that absorbs in the bone or small screw is used by the Foot and Ankle Institute to avoid the need for a metal pin protruding from the toe during recovery. Although the absorbable pin is not for everyone, it is much more comfortable than the pin protruding from the end of the toe. In certain cases, a removal of a small area of bone in the deformity area will decrease pain and limit the need for a surgical waiting period that is found with fusions. Although the toe is not as stable as with a fusion, in certain cases, an arthroplasty is the best option.
Skin creams can help maintain skin softness and pliability. A pumice stone or loofah sponge can help get rid of dead skin. Taking a warm footbath for 10 minutes two or three times a week will keep the feet relaxed and help prevent mild foot pain caused by fatigue. Adding 1/2 cup of Epsom salts increases circulation and adds other benefits. Taking footbaths only when the feet are painful is not as helpful.
Hammer Toes Pain
 Overview
Overview
A Hammer toe is a term used to describe a crooked, deviated, or contracted toe. Although the condition usually stems from muscle imbalance, it is often aggravated by poor-fitting shoes or socks that cramp the toes. Over a period of years, the tendons that move the toe up and down begin to pull the toe with unequal tension, and the toe then begins to buckle or become contracted, causing an abnormal ?v?-shaped bending of the little toes. Patients with this condition often experience pain, swelling, redness and stiffness in the affected toes.
Causes
The constant pressure a woman's foot receives in high-heeled shoes due to the force of gravity causes their feet to naturally slide down and press on the lowest point of the shoe so they are not able to receive enough space and stretch out. The result is an eventual distortion of the woman's toes. The deformity comes as a result of the shortening of muscles inside the toes because the toes become used to being in a bent position, prompting the muscles to fail to extend any further and become tightened and curbed. At first, toes may still be stretched out if poor footwear is not being worn, yet if the habit is persistent...the person's toes will eventually become used to the position they are constantly in and muscle fibers inside them will harden and refuse to stretch.
 Symptoms
Symptoms
Well-developed hammertoes are distinctive due to the abnormal bent shape of the toe. However, there are many other common symptoms. Some symptoms may be present before the toe becomes overly bent or fixed in the contracted position. Often, before the toe becomes permanently contracted, there will be pain or irritation over the top of the toe, particularly over the joint. The symptoms are pronounced while wearing shoes due to the top Hammer toe of the toe rubbing against the upper portion of the shoe. Often, there is a significant amount of friction between the toe and the shoe or between the toe and the toes on either side of it. The corns may be soft or hard, depending on their location and age. The affected toe may also appear red with irritated skin. In more severe cases, blisters or open sores may form. Those with diabetes should take extra care if they develop any of these symptoms, as they could lead to further complications.
Diagnosis
The treatment options vary with the type and severity of each hammer toe, although identifying the deformity early in its development is important to avoid surgery. Your podiatric physician will examine and X-ray the affected area and recommend a treatment plan specific to your condition.
Non Surgical Treatment
If you have hammer toe, avoiding tight shoes and high heels may provide relief. Initial (non-surgical) treatment for hammer toe involves wearing shoes with plenty of room in the toe area. Shoes should be at least one-half inch longer than the longest toe. Stretching and strengthening exercises for the toes (such as picking up items with the toes or stretching the toes by hand) are also recommended. Sometimes orthopedists recommend special pads, cushions, or slings to help relieve the pain of hammer toe.
Surgical Treatment
he basis for hammer toe surgery most often involves removing s portion of bone within the toe, to reduce the joint contracture. Depending on the direction the toe is deviated, soft tissue procedures may be necessary along with pinning the toe with a surgical wire.
What Might Cause Bunions?
Overview
 One of the more common conditions treated by podiatric surgeons is the painful bunion. Patients with this condition will usually complain of pain when wearing certain shoes, especially snug fitting dress shoes, or with physical activity, such as walking or running. Bunions are most commonly treated by conservative means. This may involve shoe gear modification, padding and orthoses. When this fails to provide adequate relief, surgery is often recommended. There are several surgical procedures to correct bunions. Selection of the most appropriate procedure for each patient requires knowledge of the level of deformity, review of the x-rays and an open discussion of the goals of the surgical procedure. Almost all surgical procedures require cutting and repositioning the first metatarsal. In the case of mild to moderate bunion deformities the bone cut is most often performed at the neck of the metatarsal (near the joint).
One of the more common conditions treated by podiatric surgeons is the painful bunion. Patients with this condition will usually complain of pain when wearing certain shoes, especially snug fitting dress shoes, or with physical activity, such as walking or running. Bunions are most commonly treated by conservative means. This may involve shoe gear modification, padding and orthoses. When this fails to provide adequate relief, surgery is often recommended. There are several surgical procedures to correct bunions. Selection of the most appropriate procedure for each patient requires knowledge of the level of deformity, review of the x-rays and an open discussion of the goals of the surgical procedure. Almost all surgical procedures require cutting and repositioning the first metatarsal. In the case of mild to moderate bunion deformities the bone cut is most often performed at the neck of the metatarsal (near the joint).
Causes
The most important causative factor is poor fitting footwear. This accounts for an higher incidence among women than men. Family history of bunions. Abnormal foot function, excessive pronation. Poor foot mechanics, such as excessive pronation (rolling inwards of the foot), causes a medial force which exerts pressure and can lead to the formation of bunions. Rheumatoid or osteoarthritis. Genetic and neuromuscular diseases, which can result in a muscular imbalance such as Down's syndrome. If one leg is longer then the other, the longer leg is more inclined to develop a bunion. If the ligaments in the feet are very weak. In some cases, bunions can occur due to trauma or injury to the feet.
Symptoms
A bulging bump on the outside of the base of your big toe. Swelling, redness or soreness around your big toe joint aggravated by footwear. Red, calloused skin along the inside edge of the big toe. Corns or calluses under the ball of the foot or where the first and second toes overlap. Persistent or intermittent pain. Restricted movement of your big toe.
Diagnosis
The doctor considers a bunion as a possible diagnosis when noting the symptoms described above. The anatomy of the foot, including joint and foot function, is assessed during the examination. Radiographs (X-ray films) of the foot can be helpful to determine the integrity of the joints of the foot and to screen for underlying conditions, such as arthritis or gout. X-ray films are an excellent method of calculating the alignment of the toes when taken in a standing position.
Non Surgical Treatment
Getting rid of a Bunion is almost impossible without surgery. Foot and toe exercises can help. Foam pads can reduce the pressure on the joint. Ice packs and anti-inflammatory medication can help reduce swelling. The progress of a Bunion can be slowed or even halted, especially if it is caused by ill-fitting footwear. Of course the best course of action is to not wear pointy-toed high-heel shoes to begin with. But if you have worn improper footwear and now want to stop the progress of Bunions. 
Surgical Treatment
For severe bunions, outpatient surgery may be recommended. Within hours after surgery, you?ll be on your way home and ready for recovery. Your foot will be bandaged following surgery and placed in a surgical shoe which allows you to remain mobile. Immediate weight bearing without the use of casting or crutches is standard post- operative recovery for bunions. In most cases, the majority of healing should occur within a few weeks and you can resume normal activity within a short period of time. Bunion surgery can both reduce pain and improve the appearance of your feet. After surgery it is important to see your podiatrist as scheduled and follow all recovery instructions.
Prevention
Make better shoe choices. If you?re a woman, avoid high-heeled footwear whenever possible (at the very least, choose shoes with heels lower than two inches), and make sure all your footwear has a wide, deep toe box. Whether man or woman, if you?re trying on shoes and your toes feel ?squished? or crowded by a particular shoe, reject that style and try another, or go for a larger size. You don?t need to invite trouble. In general, shoes that come to a point at the toe are bad news, as they tend to push the toes together into an overlapping pattern. Shoes with rocker soles will unload pressure on the bunion area. Examine your feet regularly. Note any redness, swelling or discoloration. Flex your toes and check for any stiffness. If there is any, think back to what you?ve worn or done in the past few days. If the condition persists more than a few days, or worsens, a visit to the podiatric physician is in order.
Overpronation Causes
Overpronation can affect people of all ages and it is particularly problematic for patients with high levels of activity. This problem is generally present at birth. Overpronation occurs with EVERY STEP taken. Considering the average person takes almost 8,000 steps per day and millions of steps in a lifetime, it's easy to see how the cumulative trauma from the unbalanced strain and excessive forces can lead to serious damage.
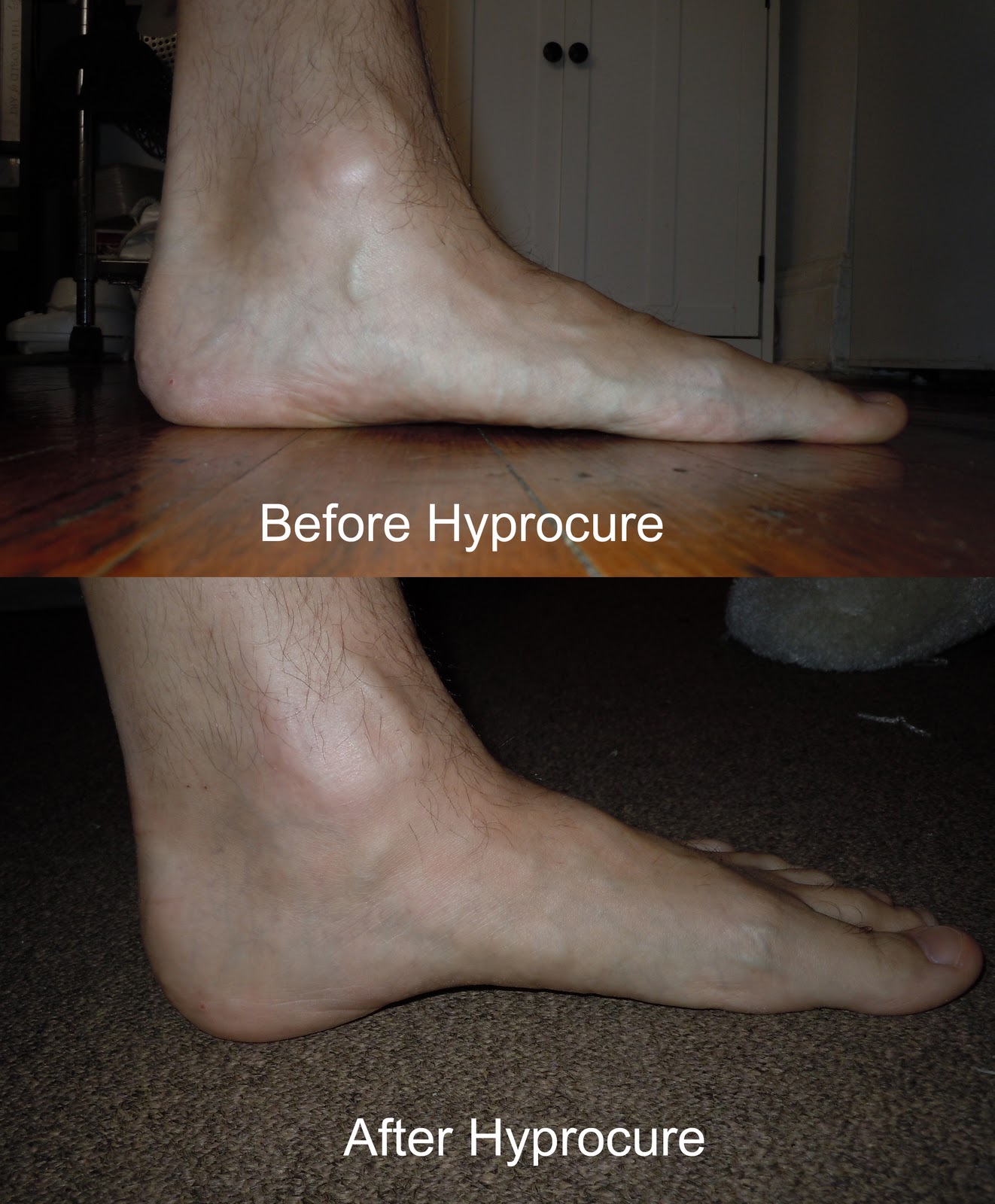
Causes
During our development, the muscles, ligaments, and other soft tissue structures that hold our bones together at the joints become looser than normal. When the bones are not held tightly in place, the joints are not aligned properly, and the foot gradually turns outward at the ankle, causing the inner ankle bone to appear more prominent. The foot moves in this direction because it is the path of least resistance. It is more difficult for the foot to move in the opposite direction (this is called supination). As we develop, the muscles and ligaments accommodate to this abnormal alignment. By the time growth is complete, the pronated foot is: abnormally flexible, flat, and its outer border appears raised so that as you step down you do not come down equally across the entire foot; instead, you come down mostly on the inner border of the foot. Normal aging will produce further laxity of our muscles that causes the pronation to become gradually worse.
Symptoms
Overpronation can negatively affect overall body alignment. The lowering of the longitudinal arch pulls the heel bone in, causing the leg, thigh bone and hip to rotate inwards, and an anterior tilt of the pelvis. Unnecessary strain to the ankles, knees, hips and back can result. Plantar fasciitis and inflammation, metatarsal pain, problems with the Achilles tendon, pain on the inside of the knee, and bursitis in the hip are just some of the conditions commonly associated with pronation.
Diagnosis
If you cannot afford to get a proper gait analysis completed, having someone observe you on a treadmill from behind will give you an idea if you are an overpronator. It is possible to tell without observing directly whether you are likely to be an overpronator by looking at your foot arches. Check your foot arch height by standing in water and then on a wet floor or piece of paper which will show your footprint. If your footprints show little to no narrowing in the middle, then you have flat feet or fallen arches. This makes it highly likely that you will overpronate to some degree when running. If you have low or fallen arches, you should get your gait checked to see how much you overpronate, and whether you need to take steps to reduce the level to which you overpronate. Another good test is to have a look at the wear pattern on an old pair of trainers. Overpronators will wear out the outside of the heel and the inside of the toe more quickly than other parts of the shoe. If the wear is quite even, you are likely to have a neutral running gait. Wear primarily down the outside edge means that you are a supinator. When you replace your running shoes you may benefit from shoes for overpronation. Motion control or stability running shoes are usually the best bet to deal with overpronation.

Non Surgical Treatment
Your podiatrist will look at your current footwear to ensure that it is both well-fitted and possessed of adequate cushioning to protect your feet. Firm heel support is advised for over-pronators, and a good fit is important to ensure that the foot as a whole is well supported as instability can exacerbate the existing problems caused by over-pronation.
Surgical Treatment
Subtalar Arthroereisis. Primary benefit is that yje surgery is minimally invasive and fully reversible. the primary risk is a high chance of device displacement, generally not tolerated in adults.
An implant is pushed into the foot to block the excessive motion of the ankle bone. Generally only used in pediatric patients and in combination with other procedures, such as tendon lengthening. Reported removal rates vary from 38% - 100%, depending on manufacturer.
What Are The Causes Of Severs Disease?
When recurring heel pain occurs in children, it is usually due to Sever's Disease, while adult heel pain is usually due to heel spurs, plantar fasciitis, or retrocalcaneal bursitis (Haglund's Deformity). Calcaneus is the anatomical name of the heel bone. Sever's Disease or Calcaneal Apophysitis is an inflammation of the growth plate located at the posterior aspect (back) of the heel.
Causes
The heel bone grows faster than the ligaments in the leg. As a result, muscles and tendons can become very tight and overstretched in children who are going through growth spurts. The heel is especially susceptible to injury since the foot is one of the first parts of the body to grow to full size and the heel area is not very flexible. Sever?s disease occurs as a result of repetitive stress on the Achilles tendon. Over time, this constant pressure on the already tight heel cord can damage the growth plate, causing pain and inflammation. Such stress and pressure can result from sports that involve running and jumping on hard surfaces (track, basketball and gymnastics). Standing too long, which puts constant pressure on the heel. Poor-fitting shoes that don?t provide enough support or padding for the feet. Overuse or exercising too much can also cause Sever?s disease.
Symptoms
In Sever?s disease, heel pain can be in one or both heels. It usually starts after a child begins a new sports season or a new sport. Your child may walk with a limp. The pain may increase when he or she stands on tiptoe. Your child?s heel may hurt if you squeeze both sides toward the very back. This is called the squeeze test. Your provider may also find that your child?s heel tendons have become tight.
Diagnosis
Sever?s disease can be diagnosed based on the symptoms your child has. Your child?s doctor will conduct a physical examination by squeezing different parts of your child?s foot to see if they cause any pain. An X-ray may be used to rule out other problems, such as a broken bone or fracture.
Non Surgical Treatment
In mild cases, elevating the heel through heel lifts in the shoes and decreasing activity level may be enough to control the pain. In more severe cases, orthotic therapy to help control the motion of the heel, as well as icing, elevating, and aspirin therapy may be required to alleviate the symptoms. In those children who do not respond to either therapy mentioned above, it is sometimes necessary to place the child in a below-knee cast for a period of 4-6 weeks. It is important for both the child and parents to understand that the pain and swelling associated with this disorder should resolve once the growth plate has fused to the primary bone in the heel.
Have I Suffered A Ruptured Achilles Tendon?
Overview
 The Achilles tendon runs from the calf muscles at the back of the lower leg and inserts at the back of the heel. A torn achilles can be a partial rupture or a total rupture. A total rupture is more common in men affecting them 10 times more than women. Injury typically occurs 30 to 40 minutes into a period of exercise rather than at the start of a session and nearly always happens from a sudden explosive movement or bending the foot upwards. Many patients are able to continue to function following an achilles rupture due to other muscles compensating although the injured leg will be significantly weaker. There are four key tests which can help diagnose a ruptured achilles tendon.
The Achilles tendon runs from the calf muscles at the back of the lower leg and inserts at the back of the heel. A torn achilles can be a partial rupture or a total rupture. A total rupture is more common in men affecting them 10 times more than women. Injury typically occurs 30 to 40 minutes into a period of exercise rather than at the start of a session and nearly always happens from a sudden explosive movement or bending the foot upwards. Many patients are able to continue to function following an achilles rupture due to other muscles compensating although the injured leg will be significantly weaker. There are four key tests which can help diagnose a ruptured achilles tendon.
Causes
People who commonly fall victim to Achilles rupture or tear include recreational athletes, people of old age, individuals with previous Achilles tendon tears or ruptures, previous tendon injections or quinolone use, extreme changes in training intensity or activity level, and participation in a new activity. Most cases of Achilles tendon rupture are traumatic sports injuries. The average age of patients is 29-40 years with a male-to-female ratio of nearly 20:1. Fluoroquinolone antibiotics, such as ciprofloxacin, and glucocorticoids have been linked with an increased risk of Achilles tendon rupture. Direct steroid injections into the tendon have also been linked to rupture. Quinolone has been associated with Achilles tendinitis and Achilles tendon ruptures for some time. Quinolones are antibacterial agents that act at the level of DNA by inhibiting DNA Gyrase. DNA Gyrase is an enzyme used to unwind double stranded DNA which is essential to DNA Replication. Quinolone is specialized in the fact that it can attack bacterial DNA and prevent them from replicating by this process, and are frequently prescribed to the elderly. Approximately 2% to 6% of all elderly people over the age of 60 who have had Achilles ruptures can be attributed to the use of quinolones.
Symptoms
The most common initial symptom of Achilles tendon rupture is a sudden snap at the back of the heels with intense pain. Immediately after the rupture, the majority of individuals will have difficult walking. Some individuals may have had previous complains of calf or heel pain, suggesting prior tendon inflammation or irritation. Immediately after an Achilles tendon rupture, most individuals will develop a limp. In addition, when the ankle is moved, the patient will complain of pain. In all cases, the affected ankle will have no strength. Once the Achilles tendon is ruptured, the individual will not be able to run, climb up the stairs, or stand on his toes. The ruptured Achilles tendon prevents the power from the calf muscles to move the heel. Whenever the diagnosis is missed, the recovery is often prolonged. Bruising and swelling around the calf and ankle occur. Achilles tendon rupture is frequent in elderly individuals who have a sedentary lifestyle and suddenly become active. In these individuals, the tendon is not strong and the muscles are deconditioned, making recovery more difficult. Achilles tendon rupture has been reported after injection of corticosteroids around the heel bone or attachment of the tendon. The fluoroquinolone class of antibiotics (such as ciprofloxacin [Cipro]) is also known to cause Achilles tendon weakness and rupture, especially in young children. Some individuals have had a prior tendon rupture that was managed conservatively. In such cases, recurrence of rupture is very high.
Diagnosis
Your caregiver will ask what you were doing at the time of your injury. You may need any of the following. A calf-squeeze test is used to check for movement. You will lie on your stomach on a table or bed with your feet hanging over the edge. Your caregiver will squeeze the lower part of each calf. If your foot or ankle do not move, the tendon is torn. An x-ray will show swelling or any broken bones. An ultrasound uses sound waves to show pictures of your tendon on a monitor. An ultrasound may show a tear in the tendon. An MRI takes pictures of your tendon to show damage. You may be given dye to help the tendon show up better. Tell the caregiver if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast dye. Do not enter the MRI room with anything metal. Metal can cause serious injury. Tell the caregiver if you have any metal in or on your body.
Non Surgical Treatment
To give the best prospects for recovery it is important to treat an Achilles' tendon rupture as soon as possible. If a complete rupture is treated early the gap between the two ends of the tendon will be minimised. This can avoid the need for an operation or tendon graft. There are two forms of treatment available for an Achilles' tendon rupture; conservative treatment and surgery. Conservative treatment will involve the affected leg being placed in a cast and series of braces with the foot pointing down to allow the two ends of the tendon to knit together naturally. 
Surgical Treatment
The surgical repair of an acute or chronic rupture of the Achilles tendon typically occurs in an outpatient setting. This means the patient has surgery and goes home the same day. Numbing medicine is often placed into the leg around the nerves to help decrease pain after surgery. This is called a nerve block. Patients are then put to sleep and placed in a position that allows the surgeon access to the ruptured tendon. Repair of an acute rupture often takes somewhere between 30 minutes and one hour. Repair of a chronic rupture can take longer depending on the steps needed to fix the tendon.
True Leg Length Discrepancy Tests
Having one leg shorter than the other is a common physical condition. It has two primary causes--structural or functional problems. Structural differences in length can be the result of growth defect, previous injuries or surgeries. Functional differences in length can result from altered mechanics of the feet, knee, hip and/or pelvis. These altered mechanics from functional leg length discrepancy often stem from having an unbalanced foundation.

Causes
There are many causes of leg length discrepancy. Structural inequality is due to interference of normal bone growth of the lower extremity, which can occur from trauma or infection in a child. Functional inequality has many causes, including Poliomyelitis or other paralytic deformities can retard bone growth in children. Contracture of the Iliotibial band. Scoliosis or curvature of the spine. Fixed pelvic obliquity. Abduction or flexion contraction of the hip. Flexion contractures or other deformities of the knee. Foot deformities.
Symptoms
The effects of limb length discrepancy vary from patient to patient, depending on the cause and size of the difference. Differences of 3 1/2 percent to 4 percent of the total length of the leg (about 4 cm or 1 2/3 inches in an average adult) may cause noticeable abnormalities when walking. These differences may require the patient to exert more effort to walk. There is controversy about the effect of limb length discrepancy on back pain. Some studies show that people with a limb length discrepancy have a greater incidence of low back pain and an increased susceptibility to injuries. Other studies do not support this finding.
Diagnosis
Leg length discrepancy may be diagnosed during infancy or later in childhood, depending on the cause. Conditions such as hemihypertrophy or hemiatrophy are often diagnosed following standard newborn or infant examinations by a pediatrician, or anatomical asymmetries may be noticed by a child's parents. For young children with hemihypertophy as the cause of their LLD, it is important that they receive an abdominal ultrasound of the kidneys to insure that Wilm's tumor, which can lead to hypertrophy in the leg on the same side, is not present. In older children, LLD is frequently first suspected due to the emergence of a progressive limp, warranting a referral to a pediatric orthopaedic surgeon. The standard workup for LLD is a thorough physical examination, including a series of measurements of the different portions of the lower extremities with the child in various positions, such as sitting and standing. The orthopaedic surgeon will observe the child while walking and performing other simple movements or tasks, such as stepping onto a block. In addition, a number of x-rays of the legs will be taken, so as to make a definitive diagnosis and to assist with identification of the possible etiology (cause) of LLD. Orthopaedic surgeons will compare x-rays of the two legs to the child's age, so as to assess his/her skeletal age and to obtain a baseline for the possibility of excessive growth rate as a cause. A growth chart, which compares leg length to skeletal age, is a simple but essential tool used over time to track the progress of the condition, both before and after treatment. Occasionally, a CT scan or MRI is required to further investigate suspected causes or to get more sophisticated radiological pictures of bone or soft tissue.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment of leg length inequality involves many different approaches, such as orthotics, epiphysiodesis, shortening, and lengthening, which can be used alone or combined in an effort to achieve equalization of leg lengths. Leg length inequality of 2 cm or less is usually not a functional problem. Often, leg length can be equalized with a shoe lift, which usually corrects about two thirds of the leg length inequality. Up to 1 cm can be inserted in the shoe. For larger leg length inequalities, the shoe must be built up. This needs to be done for every shoe worn, thus limiting the type of shoe that the patient can wear. Leg length inequalities beyond 5 cm are difficult to treat with a shoe lift. The shoe looks unsightly, and often the patient complains of instability with such a large lift. A foot-in-foot prosthesis can be used for larger leg length inequalities. This is often done as a temporizing measure for young children with significant leg length inequalities. The prosthesis is bulky, and a fixed equinus contracture may result.

Surgical Treatment
Many people undergo surgery for various reasons - arthritis, knee replacement, hip replacement, even back surgery. However, the underlying cause of leg length inequality still remains. So after expensive and painful surgery, follow by time-consuming and painful rehab, the true culprit still remains. Resuming normal activities only continues to place undue stress on the already overloaded side. Sadly so, years down the road more surgeries are recommended for other joints that now endure the excessive forces.