Overpronation Causes
Overpronation can affect people of all ages and it is particularly problematic for patients with high levels of activity. This problem is generally present at birth. Overpronation occurs with EVERY STEP taken. Considering the average person takes almost 8,000 steps per day and millions of steps in a lifetime, it's easy to see how the cumulative trauma from the unbalanced strain and excessive forces can lead to serious damage.
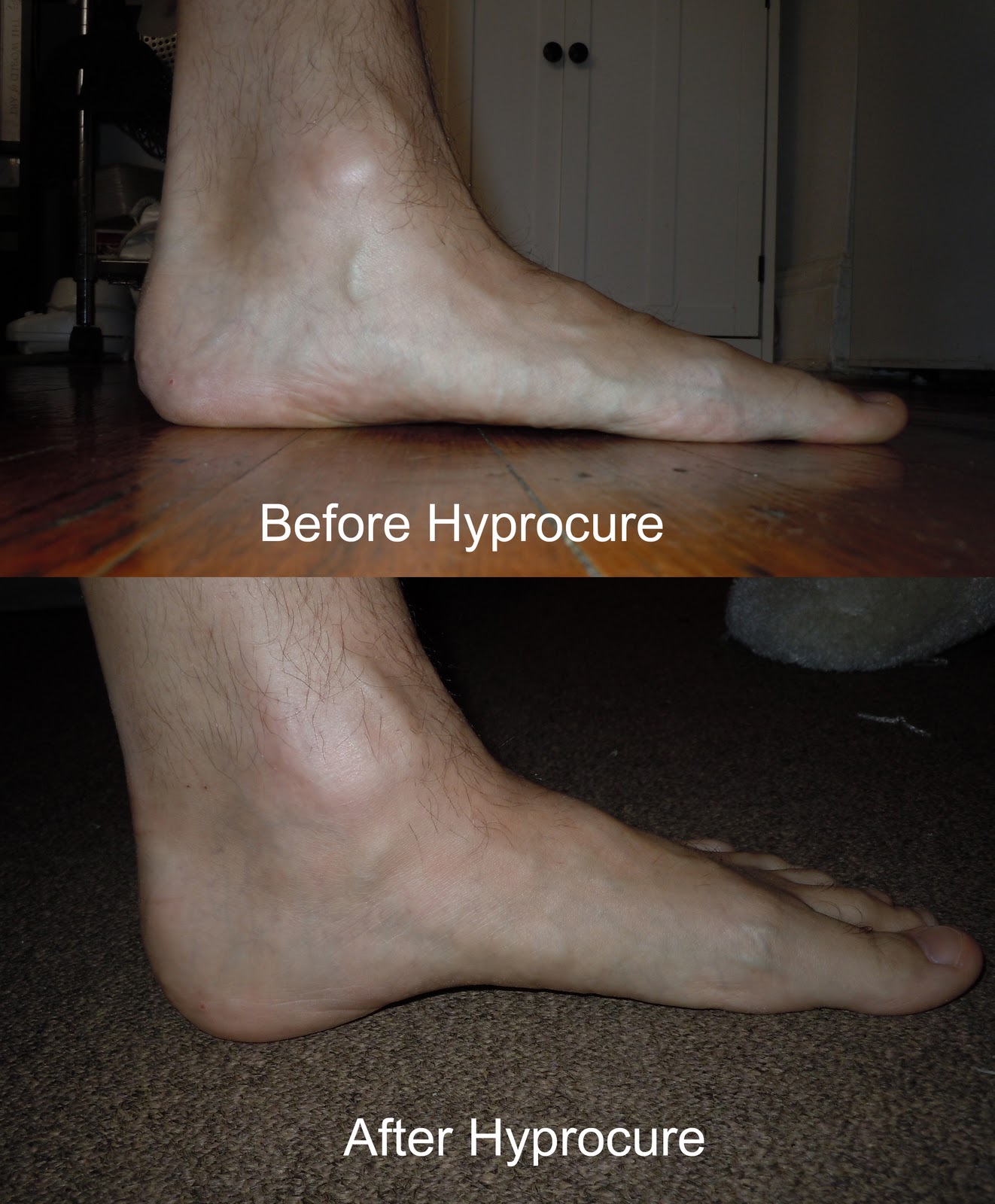
Causes
During our development, the muscles, ligaments, and other soft tissue structures that hold our bones together at the joints become looser than normal. When the bones are not held tightly in place, the joints are not aligned properly, and the foot gradually turns outward at the ankle, causing the inner ankle bone to appear more prominent. The foot moves in this direction because it is the path of least resistance. It is more difficult for the foot to move in the opposite direction (this is called supination). As we develop, the muscles and ligaments accommodate to this abnormal alignment. By the time growth is complete, the pronated foot is: abnormally flexible, flat, and its outer border appears raised so that as you step down you do not come down equally across the entire foot; instead, you come down mostly on the inner border of the foot. Normal aging will produce further laxity of our muscles that causes the pronation to become gradually worse.
Symptoms
Overpronation can negatively affect overall body alignment. The lowering of the longitudinal arch pulls the heel bone in, causing the leg, thigh bone and hip to rotate inwards, and an anterior tilt of the pelvis. Unnecessary strain to the ankles, knees, hips and back can result. Plantar fasciitis and inflammation, metatarsal pain, problems with the Achilles tendon, pain on the inside of the knee, and bursitis in the hip are just some of the conditions commonly associated with pronation.
Diagnosis
If you cannot afford to get a proper gait analysis completed, having someone observe you on a treadmill from behind will give you an idea if you are an overpronator. It is possible to tell without observing directly whether you are likely to be an overpronator by looking at your foot arches. Check your foot arch height by standing in water and then on a wet floor or piece of paper which will show your footprint. If your footprints show little to no narrowing in the middle, then you have flat feet or fallen arches. This makes it highly likely that you will overpronate to some degree when running. If you have low or fallen arches, you should get your gait checked to see how much you overpronate, and whether you need to take steps to reduce the level to which you overpronate. Another good test is to have a look at the wear pattern on an old pair of trainers. Overpronators will wear out the outside of the heel and the inside of the toe more quickly than other parts of the shoe. If the wear is quite even, you are likely to have a neutral running gait. Wear primarily down the outside edge means that you are a supinator. When you replace your running shoes you may benefit from shoes for overpronation. Motion control or stability running shoes are usually the best bet to deal with overpronation.

Non Surgical Treatment
Your podiatrist will look at your current footwear to ensure that it is both well-fitted and possessed of adequate cushioning to protect your feet. Firm heel support is advised for over-pronators, and a good fit is important to ensure that the foot as a whole is well supported as instability can exacerbate the existing problems caused by over-pronation.
Surgical Treatment
Subtalar Arthroereisis. Primary benefit is that yje surgery is minimally invasive and fully reversible. the primary risk is a high chance of device displacement, generally not tolerated in adults.
An implant is pushed into the foot to block the excessive motion of the ankle bone. Generally only used in pediatric patients and in combination with other procedures, such as tendon lengthening. Reported removal rates vary from 38% - 100%, depending on manufacturer.
What Might Cause Bunions?
Overview
 One of the more common conditions treated by podiatric surgeons is the painful bunion. Patients with this condition will usually complain of pain when wearing certain shoes, especially snug fitting dress shoes, or with physical activity, such as walking or running. Bunions are most commonly treated by conservative means. This may involve shoe gear modification, padding and orthoses. When this fails to provide adequate relief, surgery is often recommended. There are several surgical procedures to correct bunions. Selection of the most appropriate procedure for each patient requires knowledge of the level of deformity, review of the x-rays and an open discussion of the goals of the surgical procedure. Almost all surgical procedures require cutting and repositioning the first metatarsal. In the case of mild to moderate bunion deformities the bone cut is most often performed at the neck of the metatarsal (near the joint).
One of the more common conditions treated by podiatric surgeons is the painful bunion. Patients with this condition will usually complain of pain when wearing certain shoes, especially snug fitting dress shoes, or with physical activity, such as walking or running. Bunions are most commonly treated by conservative means. This may involve shoe gear modification, padding and orthoses. When this fails to provide adequate relief, surgery is often recommended. There are several surgical procedures to correct bunions. Selection of the most appropriate procedure for each patient requires knowledge of the level of deformity, review of the x-rays and an open discussion of the goals of the surgical procedure. Almost all surgical procedures require cutting and repositioning the first metatarsal. In the case of mild to moderate bunion deformities the bone cut is most often performed at the neck of the metatarsal (near the joint).
Causes
The most important causative factor is poor fitting footwear. This accounts for an higher incidence among women than men. Family history of bunions. Abnormal foot function, excessive pronation. Poor foot mechanics, such as excessive pronation (rolling inwards of the foot), causes a medial force which exerts pressure and can lead to the formation of bunions. Rheumatoid or osteoarthritis. Genetic and neuromuscular diseases, which can result in a muscular imbalance such as Down's syndrome. If one leg is longer then the other, the longer leg is more inclined to develop a bunion. If the ligaments in the feet are very weak. In some cases, bunions can occur due to trauma or injury to the feet.
Symptoms
A bulging bump on the outside of the base of your big toe. Swelling, redness or soreness around your big toe joint aggravated by footwear. Red, calloused skin along the inside edge of the big toe. Corns or calluses under the ball of the foot or where the first and second toes overlap. Persistent or intermittent pain. Restricted movement of your big toe.
Diagnosis
The doctor considers a bunion as a possible diagnosis when noting the symptoms described above. The anatomy of the foot, including joint and foot function, is assessed during the examination. Radiographs (X-ray films) of the foot can be helpful to determine the integrity of the joints of the foot and to screen for underlying conditions, such as arthritis or gout. X-ray films are an excellent method of calculating the alignment of the toes when taken in a standing position.
Non Surgical Treatment
Getting rid of a Bunion is almost impossible without surgery. Foot and toe exercises can help. Foam pads can reduce the pressure on the joint. Ice packs and anti-inflammatory medication can help reduce swelling. The progress of a Bunion can be slowed or even halted, especially if it is caused by ill-fitting footwear. Of course the best course of action is to not wear pointy-toed high-heel shoes to begin with. But if you have worn improper footwear and now want to stop the progress of Bunions. 
Surgical Treatment
For severe bunions, outpatient surgery may be recommended. Within hours after surgery, you?ll be on your way home and ready for recovery. Your foot will be bandaged following surgery and placed in a surgical shoe which allows you to remain mobile. Immediate weight bearing without the use of casting or crutches is standard post- operative recovery for bunions. In most cases, the majority of healing should occur within a few weeks and you can resume normal activity within a short period of time. Bunion surgery can both reduce pain and improve the appearance of your feet. After surgery it is important to see your podiatrist as scheduled and follow all recovery instructions.
Prevention
Make better shoe choices. If you?re a woman, avoid high-heeled footwear whenever possible (at the very least, choose shoes with heels lower than two inches), and make sure all your footwear has a wide, deep toe box. Whether man or woman, if you?re trying on shoes and your toes feel ?squished? or crowded by a particular shoe, reject that style and try another, or go for a larger size. You don?t need to invite trouble. In general, shoes that come to a point at the toe are bad news, as they tend to push the toes together into an overlapping pattern. Shoes with rocker soles will unload pressure on the bunion area. Examine your feet regularly. Note any redness, swelling or discoloration. Flex your toes and check for any stiffness. If there is any, think back to what you?ve worn or done in the past few days. If the condition persists more than a few days, or worsens, a visit to the podiatric physician is in order.